The first test that was conducted on the robot was to evaluate the accuracy of the odometry system of the robot. The University of Michgan Bi-Directional Benchmark test was performed in order to evaluate this. The robot was made to trace a 4m by 4m square path in the clockwise and anti-clockwise directions. The initial and final locations of the robot were measured using a laser distance measure for performance recording. Fig. 1 shows the results of the tests. It can be seen that the performance in the clockwise test is better than the counter clockwise test. This can be attributed to the cancelling effects of two systematic odometry errors namely unequal wheel diameters and uncertainty in the wheelbase.
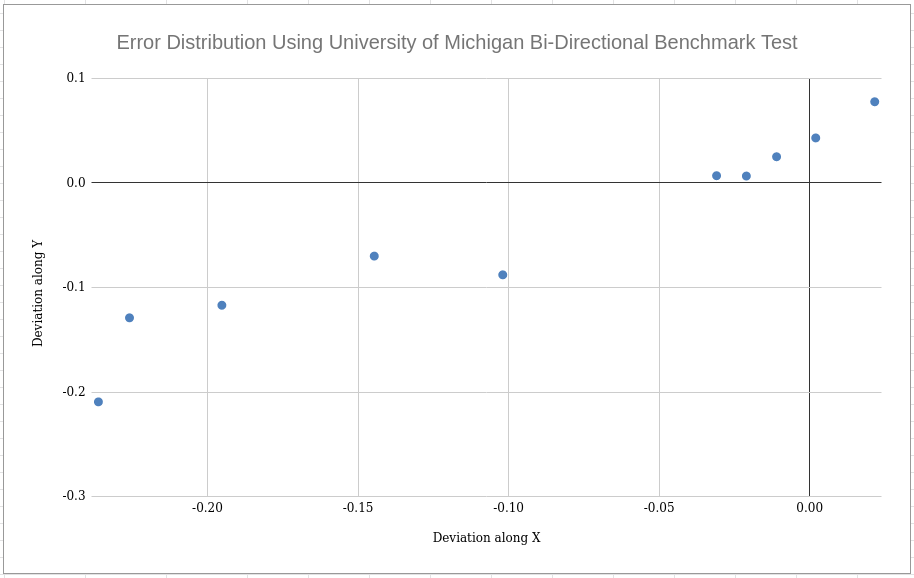
The figure clearly shows the clustering of the 5 clockwise test close to the origin while the counter-clockwise results are spread out and greater in magnitude. We intend to use the measured error metric to correct for performance only if the performance is hampered during implementation of the navigation stack.