Schedules
Gantt Chart

Gantt chart for fall semester showing schedules for work packages
Presenters
Spring
Sensors and Motors Control Lab: Dan Bronstein
Progress Review 1: Ben Kolligs
Progress Review 2: Kelvin Kang
Progress Review 3: Jacqueline Liao
Progress Review 4: Dan Bronstein
Fall
Progress Review 7: Dan Bronstein
Progress Review 8: Kelvin Kang
Progress Review 9: Ben Kolligs
Progress Review 10: Jacqueline Liao
Progress Review 11: Dan Bronstein
Test Plans
Spring Validation
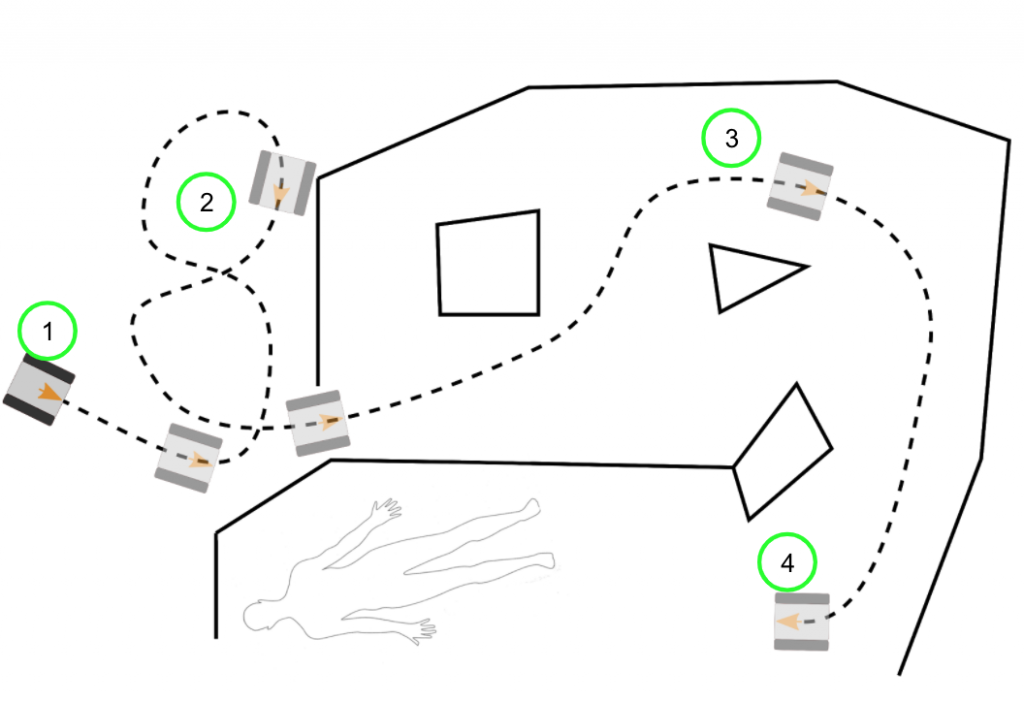
Graphical depiction of spring validation setup. Each number corresponds to the same step in “Procedure” listed below.
Goal:
Showcase our complete hardware along with the basic functionalities of our control, situation awareness, and human detection subsystems in a well-lit and smokeless room.
Location:
NSH Basement, CMU, Pittsburgh, PA
Environment:
A well-lit room no smaller than 10m2 with no smoke in the room.
Equipment:
Dragoon, visualizer, WiFi network, indoor room, room geometry/obstacle proxies(cardboard boxes, furniture, trash bins etc.), human body, external light source
Demonstrations:
- Power and Startup
- Procedure: Operator turns on robot and visualizer, then sets robot at the entrance to the room
- Validation:
- The robot connects to the remote control
- Jetson AGX turns on and connects to RealSense and Seek
- RealSense depth and RGB, Seek Thermal streams operational and stream to AGX
- VLP-16 starts scanning, Cartographer begins mapping using VLP-16 and RealSense IMU
- Visualizer turns on and begins to display 2D map and RGB stream at 10Hz (M.P.4)
- Locomotion
- Procedure: Operator moves robot forwards, backwards, using remote control at a max speed of 0.5 m/s and can turn about its location
- Validation:
- Robot moves forwards, backwards, at a min of 0.5 m/s and turns in place at a speed of 18 degrees per second (M.P.5)
- SLAM
- Procedure: Operator moves robot at a max speed of 0.2 m/s through the obstacles in the room for at least 5 minutes using the 2D map and RGB stream displayed on the visualizer
- Validation:
- 2D map of room for up to 10m from the robot is displayed and updated on visualizer; the shape of major obstacles are captured in the map (M.P.3)
- The position of the robot is displayed on a 2D map on the visualizer
- Basic Human Detection
- Procedure: Robot detects and localizes human
- Validation:
- The robot detects and localizes human 8m away within 5 seconds of complete, unobstructed entrance into the RGB and Seek FOV with 75% accuracy (M.P.0, M.P.1)
- The location of the human is displayed on a 2D map on the visualizer. Check that the centroidal accuracy of the bounding box is within 1 foot relative to the mapped room geometry
Fall Validation
Goal:
Demonstrate that Dragoon can autonomously navigate and operate in a dimly lit room and is able to determine the presence and location of a partially occluded human, which is displayed real-time on a 2D map.
Location:
NSH Basement, CMU, Pittsburgh, PA
Environment:
A dimly-lit room no smaller than 10m2.
Equipment:
Dragoon, visualizer, WiFi network, indoor room, room geometry/obstacle proxies(cardboard boxes, furniture, trash bins etc.), human body, luxmeter
Demonstrations:
- Human Detection and Localization Test
- Procedure:
- A human subject is placed in a supine position 3-7m directly in front of the robot, in profile view
- An occluding obstacle is placed blocking 0-25% of the subject
- The location of the detected human on the visualized map is noted
- Steps i-iii are repeated with varying quality of occlusion, subject pose, distance from the robot and level of ambient lighting
- Validation:
- Robot detects and localizes human who is at maximum 25% occluded 3m away in minimum 150 lux low-visibility lighting (M.P.1, M.P.2, M.N.0)
- The robot detects and localizes non-occluded humans 7m away (M.P.1, M.P.2, M.N.0)
- Human detected in real-time
- Accurate location (within 0.5m radius) of human(s) displayed on 2D map on visualizer in real-time (M.P.3, M.F.3)
- Procedure:
- Autonomous Navigation Test
- Procedure:
- Place robot in a simulated disaster scenario and let it generate paths
- Command the robot to follow a generated path
- Validation:
- Robot plans paths that avoid obstacles and generates goals in unexplored territory
- Robot follows the generated path
- Procedure:
- Autonomous Search and Rescue Test:
- Procedure:
- Place robot in a simulated 30m2 disaster scenario, with 2 human ‘victims’, and give the robot a signal to begin autonomous exploration
- Validation:
- Robot gives signal that exploration is done within 5 minutes (M.P.8, M.F.7)
- RGB stream and 2D map of room for up to 10m from the robot is displayed and updated on visualizer; the shape of major obstacles are captured in the map (M.P.2, M.P.3, M.N.0)
- 2D map is displayed and visualized in real-time (M.P.3)
- Validation of the Human Detection and Localization Test for both victims
- Procedure:
Fall Progress Review Milestones
- PR 1 (9/15)
- IR human detection Integrated into pipeline
- Local planner/obstacle avoidance implemented
- PR 2 (9/29)
- DevOps for retraining RGB and IR networks complete
- Architecture for global planner complete
- PR 3 (10/13)
- Global planner implementation complete
- Initial retraining of RGB and IR networks complete
- PR 4 (10/27)
- Global and local planners integrated with each other
- Retraining of weights for supine positions and dark conditions complete
- PR 5 (11/10)
- Entire planning stack integrated with full system, including human machine interface
- Retraining of weights finalized and integrated with full system
Full Fall Semester Test Plan (external link)
Parts List
HOWDE Parts List (external link)
Issues Log
HOWDE Issues Log (external link)
